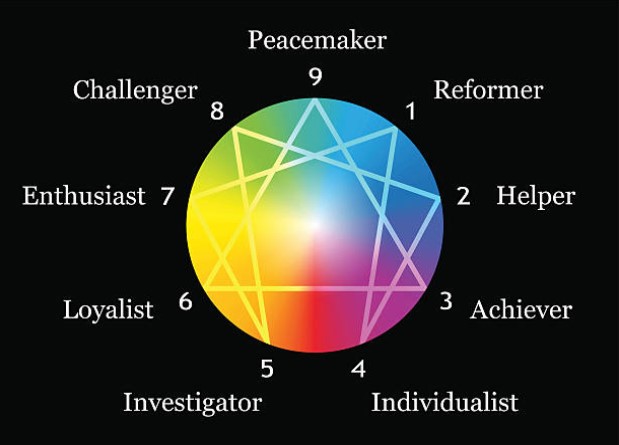
One of the most interesting ways of studying personality typology, at least for personality junkies, is by comparing different classification systems. Two of the most popular personality taxonomies, the Myers-Briggs (MBTI) and the Enneagram, exhibit a number of noteworthy correlations.
Here we’ll take a peek at some of these telling connections. I’ve also included a couple helpful summary tables at the end of the post.
Enneagram 1 Correlations
- Judging (J) types.
Ones can be found among any of the Myers-Briggs / MBTI Judging types. However, insofar as the Enneagram 1 functions as a moral change agent, Feeling (F) Perceiving (P) types may sometimes test as Ones as well.
Enneagram 2 Correlations
- Feeling (F) types.
Feelers are typically more empathetic and nurturing than their Thinking counterparts. Feelers are far more likely to resonate with the Enneagram 2, also known as “The Helper.”
Enneagram 3 Correlations
- Extraverted (E) & Thinking (T) types.
The essence of the Enneagram 3 is characteristically masculine, involving a strong drive for status and self-distinction through achievement. Although some females may test as Threes, the majority are males. On the Myers-Briggs, roughly two-thirds of males test as Thinkers (T), so by association, we’d expect to see more Thinkers identifying as Threes.
Threes also tend to be Extraverted (E), which research has linked with achievement-striving. Moreover, one could make the case that Extraverts, like Threes, are more image conscious and concerned with securing approval from others.
Judging (J) might contribute to achievement-striving as well, but Threes are also described as quite adaptable, which can be associated with Perceiving (P). Thus, the J-P preference is unlikely to be a significant contributor. Finally, other factors such as birth order may play a role, as research indicates that first-borns tend to be more achievement-oriented than later-borns.
Enneagram 4 Correlations
- INFP, INFJ.
See our post, Enneagram Type 4 (4w5 & 4w3), for an in-depth look at this type.
Enneagram 5 Correlations
- INTP, INTJ.
See our post, Enneagram Type 5 (5w4 & 5w6), for an exploration of the Enneagram 5.
Enneagram 6 Correlations
- Introverted (I) & Sensing (S) types.
Riso and Hudson suggest that the Six is an anxious type and their behaviors and attitudes can be seen as attempts to quell their anxiety. Empirical research, as well as ordinary observation, suggests that Introverts tend to be more anxious and self-conscious than extraverts, which is why Sixes are more likely to Introverted. Being more practical and less introspective / philosophical than Fours or Fives, the Six is also comprised mostly of Sensing (S) types. Learn more in our post: Enneagram 6 (6w5 & 6w7).
Enneagram 7 Correlations
- Extraverted (E) & Perceiving (P) types.
Sevens are marked by a preference for Extraversion, as well as by their use of either Extraverted Intuition (Ne) or Extraverted Sensing (Se), both of which are perceptive, explorative, and novelty-oriented functions. You can learn more about Sevens in our post: Enneagram Type 7 (7w6 & 7w8).
Enneagram 8 Correlations
- ENTJ, ESTJ.
Like Threes, the Enneagram 8 is characterized by a strong masculine essence, suggesting that Eights are more likely to be Thinking (T) types. I tend to disagree with Riso and Hudson’s association of the Eight with Ne. In my view, it seems more appropriate to link the Eight with Extraverted Thinking (Te), with ESTJs and ENTJs being the clearest representatives of this type. Hence, we’d expect Eights to exhibit the Myers-Briggs E, T, and J preferences.
Enneagram 9 Correlations
- INFP, ISFP.
The Enneagram Type 9 is slow to engage with the outside world, making this type more likely to be Introverted. Moreover, as “Peacemakers,” they are apt to be P types, preferring to adapt and avoid conflict whenever possible. This type has a more feminine essence and its most common representatives are INFPs and ISFPs.
Myers-Briggs & Enneagram Types
Introverts (4, 5, 6, 9) — Extraverts (3, 7, 8)
Sensors (6) — Intuitives (4, 5)
Thinkers (3, 5, 8) — Feelers (2, 4, 9)
Judgers (1, 8) — Perceivers (7, 9)
Enneagram Types & MBTI Preferences
Type 1 (J)
Type 2 (F)
Type 3 (E, T)
Type 4 (I, N, F)
Type 5 (I, N, T)
Type 6 (I, S)
Type 7 (E, P)
Type 8 (E, T, J)
Type 9 (I, F, P)